This distribution model is based on the Box-Cox transformation. For the given τ ≥ 0, the Box-Cox transformation is explained as follows:
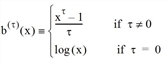
When calculating the utility, b(t)(Ria) is now included in the Logit model instead of Ria, thus the result is 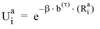 .
.
The percentage Pia of the route i in terms of the demand for time interval a is then calculated as follows:
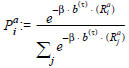
The importance of the Box-Cox model is illustrated by the two special cases below.
- τ = 0 (leads to the Kirchhoff distribution)
With these parameter settings, b(0)(Ria) = log(Ria) applies, thus the following applies to the choice:
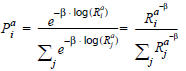
This is precisely the Kirchhoff model.
- τ = 1 (leads to the Logit distribution)
With these parameter settings, b(1)(Ria) = (Ria-1) applies, thus the following applies to the choice:
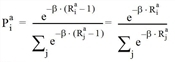
This is identical to the Logit distribution.
Illustration 90 shows the parameterization of the Box-Cox distribution model on the interface.
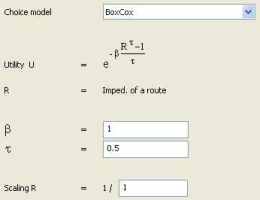
Illustration 90: Parameterization of the Box-Cox distribution model

